Essential Steps to Implement Now for 2017
As we approach the final month of 2016, it’s time to reconsider your ongoing SEO efforts and look at ways to step it up a gear for 2017. Read more
As we approach the final month of 2016, it’s time to reconsider your ongoing SEO efforts and look at ways to step it up a gear for 2017. Read more
When Onimod Global noticed significant changes in Google’s Possum updates two months ago, we knew big changes were on the way for our clients’ local search results. Read more
I’m so tired of hearing various pundits say that SEO is dead. Maybe they are merely being provocative. Perhaps they need to fill seats in their event, and so they come up with “bait” session titles like “Why SEO is fundamentally DEAD.” (Yes, that was actually a keynote title at a very popular conference last year.) Or maybe they drank their own Kool-Aid and really believe this nonsense.
While SEO is NOT dead, the way that you’re doing it might be. Does the following describe your approach? You’ve optimized your H1s and meta tags and you’ve built a few (hopefully white hat) links. Now you just sit back and watch your site rise to the top of Google, right?
Wrong. This sort of cookie-cutter approach to SEO — one that equates SEO to tuning a guitar or to following the steps to a pumpkin pie recipe — rarely works in today’s search landscape.
It’s human to want a repeatable formula to achieve a goal. The bad news is that there is no precise formula to SEO anymore. Sure, there are best practices, and a skilled SEO practitioner can greatly increase the chances of a good outcome. But we live in a world that comes with no guarantees — especially where SEO is concerned.
Of course, there have never really been any absolute guarantees when it comes to SEO. You should run away screaming from any SEO practitioner who promises one.
But for years, many operated under the illusion that if we just tweaked our title tags a little more and got just one more link, we would be rewarded with a higher ranking.
So if we aren’t able to predict an outcome from our optimization efforts, do I agree with those pundits who say that SEO must be dead?
In a way, yes. SEO in the traditional sense is dead. Outsmarting the search engines will no longer be feasible for most. But SEO does still exist, just in an evolved form.
To understand what SEO is today, let’s look at how we got here.
Remember how Google Panda shook the SEO world? Panda was released on February 23, 2011, impacting up to 12 percent of search results. Some aspects of Panda were easy to understand — the notion of thin content, for example. But other aspects were quite subtle.
Panda was the introduction to machine learning for many in the SEO industry. Google had gathered ratings from humans on the perceived quality of a website based on a set of questions. The engineers at Google then applied machine learning algorithms to extend those subjective human opinions to the rest of the web, and Google Panda was born.
It’s one thing to tweak a title tag to have a better keyword. It’s quite another thing to ask yourself whether the page will be judged as delivering a high-quality experience.
Malcolm Gladwell suggests in his book, “Blink,” that humans judge quality literally in the blink of an eye. These snap judgments, including whether a website looks “shady” or “trustworthy,” come from the gut level. It’s extremely difficult to “game” a judgment that comes from the human subconscious.
Then, on September 26, 2013, Google took artificial intelligence to another level by announcing that Hummingbird, a major rewrite of the core search algorithm, had been released. Not since the Caffeine update had there been such a significant reworking of Google’s machinery.
Most of us SEO practitioners have seen the evidence of the Panda algorithm and its spammy link penalizing counterpart, Penguin, starkly staring back at us in Google Analytics in the form of a major organic traffic drop. But when it came to Hummingbird, for most sites, there was no obvious impact. Yet when Matt Cutts said Hummingbird affected 90 percent of all searches (compare this to Panda’s 12 percent), it was clear something big had happened. But what?
A clue had come in the form of a Google demonstration of hands-free conversational search at Google I/O: the “OK Google” voice command.
It was thrilling to see we were one step closer to realizing a Star Trekkian future where we could speak to our machines using natural, everyday language, and they would not only understand us but also answer back.
But under the covers, to handle conversational queries correctly, search engines like Google needed to understand the intent of the query, not just the words in it.
We had made the leap from “words” to “concepts.” Understanding the meaning behind words, as well as the relationships between the words in a given topic, is known as semantic search.
If this ability to understanding meaning and intent behind words is not “artificial intelligence,” I don’t know what is. Google Now is only the beginning. We’ll soon be talking to our computers more than we will be typing at them.
And search continues to evolve. Last year, Google announced it had released RankBrain, which is machine learning that helps Google understand and process search queries. RankBrain has been particularly useful to Google in long-tail queries, which are often conversational and new to Google. Even today, 15 percent of search queries entered into Google are new searches never seen before. RankBrain is being run across 100 percent of all Google search queries; it’s become pervasive.
RankBrain is another step in the evolution of the true realization of semantic search.
With semantic search, Google can understand what an article is about. We see evidence of this when articles rank for keywords that are not found anywhere in the article (or in anchor text pointing to the article). One simple example of this is the search for “internet marketing,” which returns Quick Sprout’s guide to online marketing in the number one position. The word “internet” is not found anywhere in the guide.
So if you can rank for a keyword without having it in your title tag or in any of the usual optimization targets (such as the URL and H1), how much does on-page optimization really matter?
In a recent study that analyzed one million Google search results, Backlinko found that the correlation between a given keyword in the title tag and the ranking for the search with that keyword was much smaller than expected.
It used to be important in SEO to have an exact matching keyword (or at least close to it) in a title tag in order to rank for that particular search query. What the Backlinko study illustrated is that Google is now significantly better at understanding the context of your page, and thus you don’t need to be explicit with the keyword you’re targeting, especially if your content clearly discusses the related entities involved in the topic.
What do I mean by “entities?” Let’s take an example. If you have an article on list building, it’s likely that the keyword “list building” would appear, but it is also likely that terms related to list building would also be present in the article, such as “subscribers” and “email.” These terms are relevant to our topic of list building, s0 it’s reasonable to expect them to be in our article.
We know that “email” adds specificity to “list building.” For example, it further defines the type of list (it’s not a Facebook audience). So “list building” and “email” have a relationship which creates meaning beyond just the words. So in the search industry we use the term “entities” to describe these “things” that have a meaning and often have a real-life existence and relationships with other entities.
Incidentally, this may be why longer-form content is performing better in organic search today, because the content describes more fully the topic and has more of the related entities present.
My favorite new tool for exploring entities and relationships between topics is Searchmetrics’ new Topic Explorer, which I demonstrated live last week at Pubcon in the Advanced Keyword Research session. Since Google has gone beyond keywords into entities, we too need to go beyond traditional “keyword research” into “entity research.”
Winning at SEO today is not about figuring which buttons to push. Once you have done the technical due diligence to make your site Google-friendly, you need to put on your marketer’s hat and give up the old school SEO “tactics” that used to work but don’t anymore.
Yes, title tags should have keywords and should be written to entice the user to click through, but you no longer need to worry about getting the keyword precisely right. And it goes without saying that keyword stuffing your tags is not a valid practice, nor has it ever been.
Instead, focus on the experience of your site: How can you make it better?
Get deep into the mind of your ideal visitor and figure what makes them tick. What are their frustrations? What are they looking for? You need to solve for your user, not for the search engine.
Your focus should be on creating remarkable content that is clearly head and shoulders above its competitors, and then on getting users to rabidly consume and share that content.
Content has always been important with SEO. Now more than ever, extraordinary and noteworthy content that creates a conversation or adds massive value to existing conversations is an essential prerequisite to successful SEO.
“SEO is dead. Long live SEO!”

When it comes to success with paid search, it’s not just about ad copy. You have to pay attention to your ad extensions and your landing pages as well.
In this article, Mona Elesseily from Search Engine Land discusses the specific ad features and page elements that searchers/shoppers want when they’re shopping online. She also covers ways to also incorporate the elements using PPC/paid search.
Seventy-eight percent of shoppers want images.
Shoppers respond well to images. It’s the reason Google has been and is continuing to increase the number of images we see on search engine results pages (SERPs). It’s also the reason good online retailers allow us to zoom in and view products from different angles.
An awesome way to increase the number of images in the SERPs is to use product listing ads (if applicable). We love how product ads allow us to take up space and show more than one product in the shopping pack. We like adding ad annotations like price drop alerts (in Bing), merchant badges and product ratings to make ads pop even more and grab buyer attention.
Focusing on feeds now will pay dividends in the future, as shopping feeds will likely appear in more places in the SERPs (Think image search and local ad units), and feed-based advertising will become much more commonplace. It’s a good idea to prep for opportunities that will come along in the not-too-distant future.
Sixty-nine percent of shoppers want product reviews.
It’s a great idea to have them on your site and also to incorporate them into PPC ads using review extensions. Review extensions are finicky, as there are lots of search engine policies related to posting “accurate and current” reviews. It’s not uncommon to have ads disapproved a few times before they get approved.
It’s worth noting that reviews can be no more than 12 months old to appear in Google Trusted Stores, and hence, review extensions. Consistently ask customers to review products, so that review extensions (and seller ratings, for that matter) will continue to appear in your account.
Forty-six percent of shoppers want side-by-side product comparisons.
These are effective ways to compare your company products or to compare your product against the products of competitors. Graph or table format tends to be the easiest to read and allows shoppers to better digest information.
Here’s an example from Phillips and some of their natural light wake-up lights:

Personally, I like to highlight (or badge) the most popular product. Badging is very effective in improving online conversions, and I’ve seen increases of more than 20 percent when tables include a badge. In the example below, the pro version of the product is the most popular and is denoted using the color blue.

This example would have been even better if the blue column were marked “best seller” (or similar wording).
Forty-two percent of shoppers want customer testimonials.
I find these very useful, especially if there’s a striking difference between you and your competitors.
I work with a company that manufactures a product that’s more expensive than their competitor’s product. Their testimonials highlight other benefits and do an effective job of making the extra cost negligible. The “negative” is offset by the awesome knowledge and customer service.

Testimonials effectively encourage people to bite the bullet because they know their overall experience will be good and that they’ll be thrilled with their purchase.
Thirty percent of shoppers want video product demos.
This is especially true if the product is complicated or hard to understand. For example, let’s say you sell car replacement parts, and the parts are tricky to install. Here’s an example of videos from 1aauto.com.

In PPC, video extensions are a good option to consider. At this point, these are only available in Bing.
Twenty-two percent of shoppers want live chat with a shopping assistant.
A good option for this is the ActionLink extension in Bing. We’ve seen higher ad engagement as a result of including this, especially in industries where people have a lot of questions, like home renovations.
Nine percent of shoppers want links to media coverage of company products.
On sites, people often include “as seen on” and other such credibility indicators. Be sure to also include links to media coverage. I test short video clips of the media coverage on pages. Sometimes, having clips in addition to links to media coverage boosts conversions.

Google’s algorithms rely on more than 200 unique signals or “clues” that make it possible to surface what you might be looking for. These signals include things like the specific words that appear on websites, the freshness of content, your region and PageRank. One specific signal of the algorithms is called Penguin, which was first launched in 2012 and today has an update.
After a period of development and testing, Google are now rolling out an update to the Penguin algorithm in all languages. Here are the key changes you’ll see, which were also among webmasters’ top requests to them:
The web has significantly changed over the years, but webmasters should be free to focus on creating amazing, compelling websites. It’s also important to remember that updates like Penguin are just one of more than 200 signals Google use to determine rank.
For more information on the above changes and how it benefits you, contact an Onimod Global Digital Marketing expert today.
What is Social Media Marketing?
Social media itself is a catch-all term for sites that may provide radically different social actions. For instance, Twitter is a social site designed to let people share short messages or “updates” with others. Facebook, in contrast is a full-blown social networking site that allows for sharing updates, photos, joining events and a variety of other activities.
How Are Search & Social Media Marketing Related?
Why would a search marketer — or a site about search engines — care about social media? The two are very closely related.
Social media often feeds into the discovery of new content such as news stories, and “discovery” is a search activity. Social media can also help build links that in turn support into SEO efforts. Many people also perform searches at social media sites to find social media content. Social connections may also impact the relevancy of some search results, either within a social media network or at a ‘mainstream’ search engine.
As long as you think of search and social media as separate projects and place them in silos, you won’t see the maximum impact for your business. Create a cross-functional process between the search and social so that you can integrate the search learning into social media, and the social media learning into search. The search keywords, social conversations, and the target audience behaviors are some of the key information that you should be sharing between the two.
The Bottom Line
It’s vital that you understand social media marketing fundamentals. Besides increasing brand awareness and establishing the legitimacy of the brand, social media marketing can affect the bottom line of a business by increasing sales. Learning about the importance of social media for marketing should also underscore why these efforts need to be continuous and the harm it does when social media marketing isn’t up to consumer expectations. Long story short, social media marketing is something that every business needs to do and needs to do well.
An integrated social media platform can enhance marketing campaign effectiveness, help improve brand building across the enterprise, and make a real impact on sales and the bottom line. Integrated social capability brings another great benefit by keeping the enterprise updated with the latest innovations in social media. Sites such as Facebook and LinkedIn are constantly innovating and updating their collaboration tools, content-sharing formats, etc. With integrating social capability, customers don’t need to change business functions in sales or marketing to catch up with these changes.
In today’s much-hyped world of social media marketing, integrated social capability can make a direct and positive impact on the business. Leveraging the power of content and social media marketing can help elevate your audience and customer base in a dramatic way. But getting started without any previous experience or insight could be challenging. Speak to an expert today at Onimod Global to learn how YOU can leverage your company’s social media marketing.
That’s right — position #1, the elusive goal for so many SEOs, may not matter so much anymore. Crazy statement, right? Trust me… follow me for just a minute.
The screen shot below shows what Google refers to as a featured snippet, also known as a direct answer. (It’s also one I searched recently when baking, realizing I forgot to buy self-rising flour and hoping I wouldn’t have to go back to the store. Anyway, moving on… )

As you can see, the direct answer information is displaying above the initial search result. I don’t even have to click on the link to find the answer I need. I’m able to see that if I pull the baking powder and salt out of the cupboard, I can save myself a trip to the store.
While this is great for the end user, it means that MyRecipes.com provided me the information I needed, but I never visited their site. In many instances, however, the consumer is still going to visit the website because they need more information than what’s displayed in the direct answer.
So why does position #1 not matter as much? While the direct answer shown above does come from the #1-ranked website for the search query, it doesn’t always work this way. The direct answer is pulled from the site with the best answer, and Google doesn’t seem to care how it’s ranked.
In the example below, the featured snippet has been pulled from the #3-ranked result. (Not that I’ve ever searched this particular query in a sleep-deprived moment during the past year… )

Can you imagine the difference in traffic for the #3 result with the direct answer vs. the #1 result without? Normally, the top organic ranking would have the highest click-through rate; however, the direct answer is likely taking traffic from the top result here (if not getting the majority of the clicks).
It’s important to optimize the content on all of your properties, not just your website. Yes, you really do need to include full content descriptions on your social profiles, because you never know what Google’s going to deem the best candidate for a direct answer.
In the example below, Google has chosen a featured snippet from a video on Pottery Barn’s YouTube channel for the search query, “how to hang drapes.” A page from Pottery Barn’s website that contains tips and how-tos for hanging drapes is #1 in the SERP — but because they’ve optimized their YouTube video description, it’s been selected as the direct answer. This benefits Pottery Barn in the long run, because now they have more real estate above the fold.
The video is embedded in their website, along with additional supporting content on hanging drapes. Pottery Barn’s how-to guides provide a great information resource for customers, and that’s likely why Google’s rewarding them with both the featured snippet and the #1 position in the SERP.

The featured snippet is pulled from the video description on YouTube:

So, what does all of this have to do with your SEO content strategy? When you provide useful information that’s easy to follow and understand, it could be used as a featured snippet in Google search results. If that happens, you will likely see a boost in traffic to your site — perhaps even more than the top organic result.
If you have optimized your site and your social channels, you can potentially gain a bigger portion of the SERP landscape through the featured snippet and position #1 ranking. However, even without #1, if you have the featured snippet, you are essentially the new #1.
Now that you understand the reward, you need to determine how to go after the direct answers. Start by searching Google for some of your target keywords (especially long-tail variations that take the form of a question) and find out if these queries trigger a featured snippet.
If these searches do produce direct answers, look at the sites that are obtaining them and evaluate what they’re doing differently. If you have the right information on your site to answer the query, double-check your setup. Do you have a dedicated page for each question with comprehensive, high-quality content? Or do you answer the question as part of a larger FAQ page? You may need to make some changes in order to win the featured snippet placement.
Direct answers are still relatively new, and they’re not on all queries. You may find that they’re starting to add them for queries related to your vertical, but the number of questions being answered is limited. Remember, even if a particular query doesn’t trigger a direct answer now, it may in the future — so you can always start creating content with that in mind.
Keep in mind that featured snippets are more commonly found on informational queries rather than transactional ones, so optimizing your content for direct answers will primarily be for the purpose of capturing searchers at the top of the funnel. In other words, plan your content accordingly; don’t try to use product pages to obtain featured snippets unless it’s appropriate to do so.
Position #1 isn’t as important as being the direct answer. Focus on creating great content that’s useful to your audience, and target the queries that would send someone to your site. While simple answers such as “what is a substitute for self-rising flour” may not drive tons of traffic, queries like “how to hang drapes” will likely drive traffic and quite possibly revenue in time.

Whether you work in SEO or PPC, you’ve likely noticed a new trend emerging in your search reports: a rise in longer-tail searches and question-based search phrases. The likely culprit? Voice input.
Voice search is easier than text input; we all know this. We can speak something much more naturally than we can type it. Most of us are looking for a fast fix or a way to make multi-tasking more efficient, and conversational user interfaces fit that bill perfectly.
Whether we want to ask Alexa to clarify a recipe while cooking, ask Siri for directions while driving or run quick searches during the commercial breaks when second-screening, we’re all getting increasingly comfortable using voice search and digital personal assistants.
Take a look at the rapid adoption rates that Search Engine Land reported on back in December:

The vast majority of folks reported adopting conversational search just within the last several months, showing how dramatically it is growing.
Why does this matter?
There’s an obstacle that brands face when adjusting to voice input for search. The obstacle is that we will turn this easy input into a complicated problem because we haven’t adjusted for it.
Here are three simple steps you can take today to prepare.
Do you follow the comedian John Oliver? I love how good he is at skewering companies or people who are doing things they shouldn’t. Recently, he did a report on the problem of mistaken identity in credit reporting with the three big credit reporting companies.
John Oliver’s investigation revealed that as many as 10 million people in the United States have major errors on their credit reports as a result of mistaken identity, but the major credit reporting companies (Equifax, Experian and TransUnion) have no system in place for fixing these errors which cause a lot of havoc in people’s lives.
Here’s what he did:

He suggested his viewers visit parody sites his team created at equifacks.com, experianne.com and tramsonion.com. Because, as he said, “It would clearly be a horrible thing if these actual companies were mistaken for these fake companies. But don’t worry – 95 percent of the time, that won’t happen. And apparently that’s good enough, right?”
While this is a hilarious parody, we do need to take into account variations in pronunciation when it comes to voice search, since the margin of error here can be quite vast.
I could search for these brand names and still come across the parody sites, like here:

As you can see, this is not ideal for the credit company’s brand.
I’m going to walk you through a true example, and this is your cautionary tale.
I did a voice search on Cortana on my desktop for Bobbi Brown makeup. I noticed that Cortana spelled “Bobbi Brown” differently from the brand name:

Here’s what the SERPs looked like:

Great job on the shopping ads here, and the organic results were on point, too. In this case, misspellings had been accounted for within the search strategy.
But what about brands that are not in English?
Let’s take Yves Saint Laurent as an example. I searched for “show me Yves Saint Laurent bags” using both Siri and Cortana:

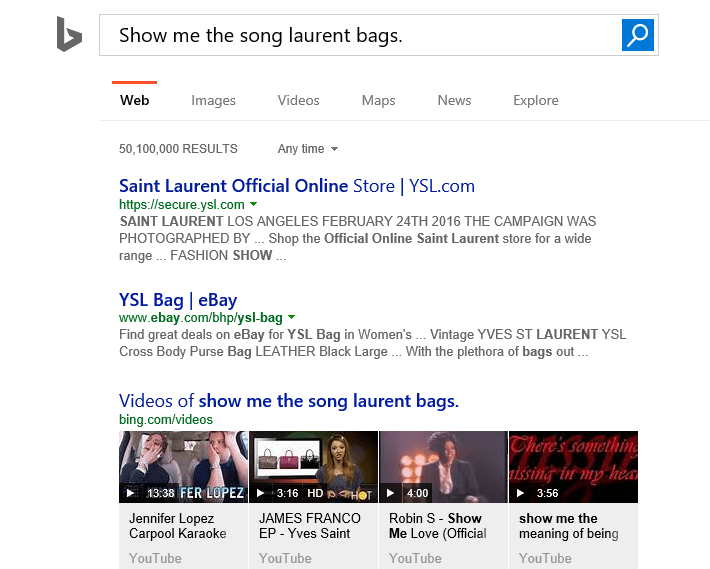
Cortana did much better here than Siri did, but the variability in pronunciation means that we can’t count on voice search getting it right every time — at least not for a while.
Advertisers need to anticipate these issues and commit some time to resolving the voice search picture for their brands.
What can you do?
Natural language shows intent more strongly.
When you type a search, you use computer language — “Bahamas vacation deals,” for example. When you speak a search, you use your own language: “What are some Bahamas vacation deals for June?” or “How much does it cost to fly to the Bahamas?”
The advantage of this is the degree of specificity. That’s also where brands can stumble.
If your listing in the SERPs for one of these specific queries is a generic page, chances are you’ll lose the click. To boost your chances of winning, make sure you offer search results that can answer the query most closely.
For example, here are three of the ads that showed up for a conversational search for “What are some Bahamas vacation deals for June?” Which one would you have clicked on?

The third ad mentioning the “summer sale” has a very high level of relevancy, and it is the only one that factored in the specific timeline mentioned by the searcher. That’s the one I would have picked!
What can you do?
Of course, you’re showing up for branded searches or transactional searches directly asking for your product. But what about being helpful to your customers by answering their questions with information you have to share?
As you know, content marketing helps brands build loyalty. When it comes to conversational search, it also helps you show up for long-tail queries, which is another aspect of voice search that is becoming more critical.
Since voice search queries have been shown to frequently contain question words, marketers could benefit from informational creative that addresses top-of-funnel queries, as well.
While they may not immediately be transactional, this content could help build your brand’s goodwill and engagement levels.
For example:

What can you do?
Think of the last few searches you did using voice. How often are you using it? This is a great time to get a jump on voice search and voice inputs, as we all try to figure it out together as an industry.
The early adopter gets the advantage, so why not get the conversation started at your company?

Article H/T: Search Engine Land. Image: Alexander Supertramp / Shutterstock.com
SimilarWeb data argue that search remains the dominant source of traffic to desktop sites. Read more
You’re about to launch your new website. You have a fantastic idea/product and a great team. You understand the basics of SEO. But you think you cannot do SEO without a live site. It is impossible, right?
Actually… no!
It is more than possible. In fact, it is critical.
Way too often, website owners fail to do pre-launch SEO. This results in a poor index of their site. So instead of jumping up in the rankings, their site is ignored by Google and the other search engines and buried deep in the results. They then are stuck with a long climb, even, in many cases, for their branded terms.
Following are seven smart ways to jump-start your SEO before your site launch, and I’m going to show you exactly how to implement each one.
Creating a strong, optimized “coming soon” page should be one of the very first things you do as you contemplate your new site. There are lots of reasons why this is important:
Update the kit frequently. Not only will this ensure that it is more complete, but it’ll lead search engines to see fresh content here regularly. Make sure to do the kit on standard web pages so that it can be linked to and ranked.
If you’re still not convinced, remember: Google has advised webmasters to use a “coming soon” page in the past.
It is absolutely critical to start building your social media community before your site launches. You want to make sure that you already have a loyal following who is invested in your business when the launch happens.
By engaging your audience on relevant social media platforms and sharing great content, you are fostering trust in your brand and business and furthering your reputation as an authority.
Make sure you have complete profiles on all of the biggies (Twitter, YouTube, Facebook, LinkedIn, Google+) and any of the other platforms that specifically speak to your target audience.
Connect each profile with your “coming soon” page, and make it simple for people to follow your social media presence and get updates about the launch by just clicking a button.
Well-optimized, actionable content will bring tons of organic traffic to your site even when it’s still very new. There is no shortcut here; you need your content to be high-quality. And while you need to keep that content coming long after the site has launched, you should already have a healthy content reserve in place at launch.
This is because the web crawlers will be visiting your site to index it right away, and you want them to have plenty of information-rich content to index from day one. Long-form content, in particular, is going to provide a depth to your brand-new site that can’t be replaced, and it simply ranks higher in search results.
Also, in some cases, it is a good idea to start a blog pre-launch. This will allow you to do pre-launch announcements, add continual fresh content and build up a little SEO authority and buzz.
Hopefully, you will also be able to attract some links. In addition, when you start doing press releases, you will have your blog ready so that news sources and consumers can refer to it for more information.
Along these same lines, you need multiple pages within your site, and each must be optimized. Include long-form, high-authority content that your target visitors will use on each page. Don’t reinvent the wheel from page to page; instead, make sure each page is focused and useful.
Remember to use keywords, long-tail keywords in particular (Your site will not rank for large terms right away), on every page and in page titles. Put your keyword database for your site to work on every page. You want to make sure you’ve created a fantastic, optimized page for every possible aspect of the business before the launch happens.
Then, when you go live, search engines will index the pages properly and (hopefully) give you some initial rankings.
When I bring up guest blogging to build links to your domain, I’m not talking about spammy self-promotion. I’m talking about producing some of your best work to share with the audiences of sites you admire.
When done properly, guest blogging is a fast, powerful way to generate traffic to your site and leads for your email list. It also allows you to build your credibility and eventually become an influencer.
Search for the best guest blogging opportunities by checking the sites in your niche and finding out what kinds of guest posts they’d like to see. You can also search out the keywords and phrases that you want to be associated with to see where people read and write about those topics.
Finally, you can simply search for “guest blogging opportunities” or “write for us,” along with your niche keyword or phrase.
This step is critical before your launch. A directory simply lists sites and businesses and breaks them down using categories and sub-categories.
By getting your website listed in the right ones before launch, you will have built authority to your “coming soon” page that will be transferred to the rest of your pages when they go live.
If the directory is well-known and widely used in your area of business, it will be worthwhile. But don’t pay for just any directory. Make sure you know the directory is a real powerhouse in your field before paying.
These core sites include, but are not limited to, the following:
There is a great service called KnowEm, which can help you do this more quickly.
There are a lot of things you can do prior to launch; I have not added every idea under the sun here. But this is generally a good checklist to build upon:
The time immediately following your launch is crucial to your success. This is the time you must monitor your traffic, assess your results with metrics and test/tweak your strategy. Don’t lose time here. Stay on top of it.
Watch for red flags like these:
Also, make sure you have a great launch strategy. This will be the time to really hustle.
One of the worst things you can do is launch an unoptimized site. Ask yourself this: How many websites do you think are launched a year?
You want to stand out, and to do it right, you need to have an optimized site. And not just optimized a little, you need to really put in the time. If you are new to the online space, make sure you work with someone with experience, so you have an optimized site and a great pre-launch SEO strategy.

Call Us: 888-263-7046
159 N. Sangamon St.
Suite 200
Chicago, IL 60607
